In 2015, BT announced plans to stop the purchase of ISDN lines in 2020 and to officially switch off ISDN in 2025. The 5-year phase out has officially begun and many businesses and homes are starting to think about making the change. In this guide, we’ll teach you all about ISDN, how to prepare for the switch and what alternatives are available for you and your business.
What is ISDN?
ISDN stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. It’s a set of communication standards that uses digital transmission to make phone calls, video calls, transmit data and other network services over the circuits of the traditional PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network).
ISDN was introduced in 1986 by BT. It replaced and updated old fashioned landlines to digital lines and added features that weren’t available with a classic telephone system.
How does ISDN work?
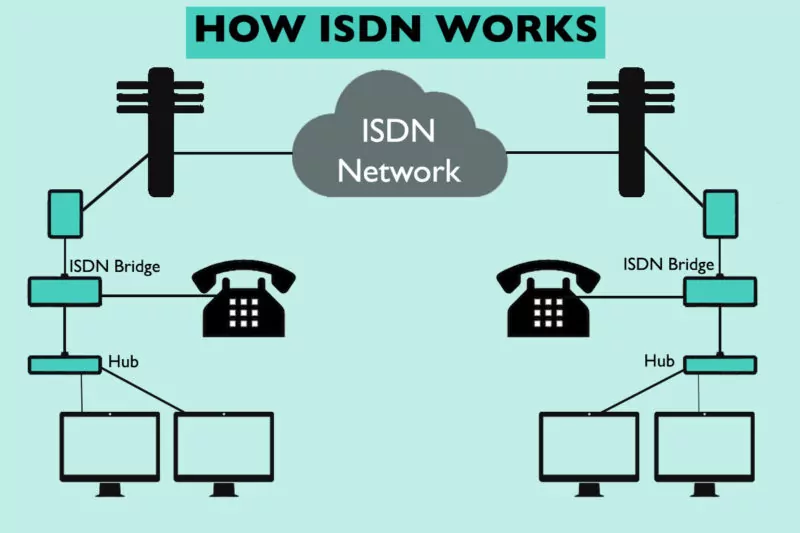
ISDN splits the traditional copper telephone line into multiple digital channels. These channels operate concurrently on a single copper line, allowing multiple phones to make and receive calls simultaneously using one physical line.
There are 2 main types of ISDN: BRI or PRI.
BRI
BRI stands for Basic Rate Interface and is an ISDN configuration primarily used for voice-grade telephone services. It is made up of 2 B-channels (bearer channels), at 64 kbit/s and 1 D-channel (delta channel), at 16 kbit/s.
Let’s break this down into simple terms: A B channel is used for voice and user data. A D channel is a combination of data, packet networking and control and signaling. Combined, these channels help BRI control the transmission of information. BRI is used in many countries and is typically installed in residential areas or small businesses.
PRI
PRI stands for Primary Rate Interface and is used for carrying multiple Digital Signal Zero (DS0) services and data between the ISDN network and a user. PRI is commonly used by large companies, offices and enterprises.
ISDN Switch Off: What It Means For Your Business
While the infrastructure of ISDN has been significantly upgraded since its inception in 1986, the network has remained relatively unchanged and is now a little outdated. In particular, broadband internet connection speeds are a lot faster and at a higher level than ISDN and ISDN can no longer compete.
BT has heavily invested in VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) in recent years. Following these developments, BT realised that it doesn’t make sense, both financially and strategically, to keep furthering the ISDN network. By concentrating on up-to-date technology like VoIP, BT can focus their resources into building services for the future and meeting growing demands from both businesses and residentials.
Traditional ISDN lines also offer little flexibility. With ISDN, businesses are tied to physical locations. More and more companies are looking for cloud-based systems that are scalable and flexible for remote working and company/building expansions. IP technology is a better choice for these requirements and around 40% of businesses have already moved to VoIP systems.
What can I switch to?
There are two options that you can switch to: VoIP or SIP. What this boils down to is whether you want to use a hosted PBX system or an on-premise PBX system for your home or business. If you want to buy a whole new phone system when you make the switch from ISDN, choose VoIP. If you want to keep your current system when you make the switch, go with SIP.
Both VoIP and SIP are the future of telecommunications and simply need an internet connection to work. Making the switch with these systems is cost-effective, easy and fast to setup and no physical lines need to be installed. Deciding which system to go with is up to you and what you need/want for your business.
Need support?
Talk to us today
Contact us
How to switch from ISDN to hosted VoIP
VoIP uses the internet to make and manage voice communications and additional call and multimedia services. If you already have ISDN lines and don’t want to commit to an on-premise phone system, choosing a hosted VoIP phone system is the best option for you. There’s no need for any physical lines or hardware (other than configurable handsets), and everything is looked after and managed by your provider. With VoIP, your business phone system is more scalable and flexible to your business’s needs. It also reduces call rates, maintenance costs and comes with innovative call and media features.
Switching from ISDN to VoIP is extremely simple. First, you need to find out what your business needs/wants and how many phone extensions you’ll need. If this number changes, your provider will add and remove as necessary. Once you’ve done some research about telecom providers, choose a supplier and the equipment, and set up is taken care of for you.
Two things you’ll need to consider is if your internet connection can deliver VoIP and if your office phone system can support VoIP. If your internet speed doesn’t have enough bandwidth to deliver voice and other features, you’ll need to upgrade it to one that does. Most new office phone systems support VoIP but if yours doesn’t, you’ll have to replace it with an IP phone system.
If you want to get started with VoIP from Gradwell, we offer 3CX and Wave.
How to switch from ISDN to SIP
SIP stands for Session Initiation Protocol and is one of the possible protocols used in VoIP communications. SIP and SIP trunks are a great on-premise solution for a phone system, as it uses virtual phone lines rather than physical lines. You also have a choice of systems when you use a SIP Trunk, like 3CX and Direct Routing for Microsoft Teams.
So, what’s the difference between SIP and SIP Trunks? SIP is the set of rules that allows you to make and end connections for data and voice transfers over the internet. SIP Trunks is the service that allows you to use this protocol on a public network.
SIP Trunks are becoming the most popular alternative to ISDN, due to their flexibility, speed, quality and lower costs. Making the switch to a SIP Trunk is a smooth process and is very similar to what we’ve discussed above. Once you’ve picked a SIP Trunk provider, they’ll take care of everything for you.
You’ll need to plan to port your numbers before you switch off ISDN for good. Number porting is the process of moving your telephone number from one provider to another. It’s a good idea to do this if your business uses location-specific phone numbers or if you want to keep all your existing numbers. Number porting is something that most providers will offer but it can take up to a few weeks depending on the amount of numbers you want to port and your porting agreement with your previous provider.
What impact will this have on businesses?
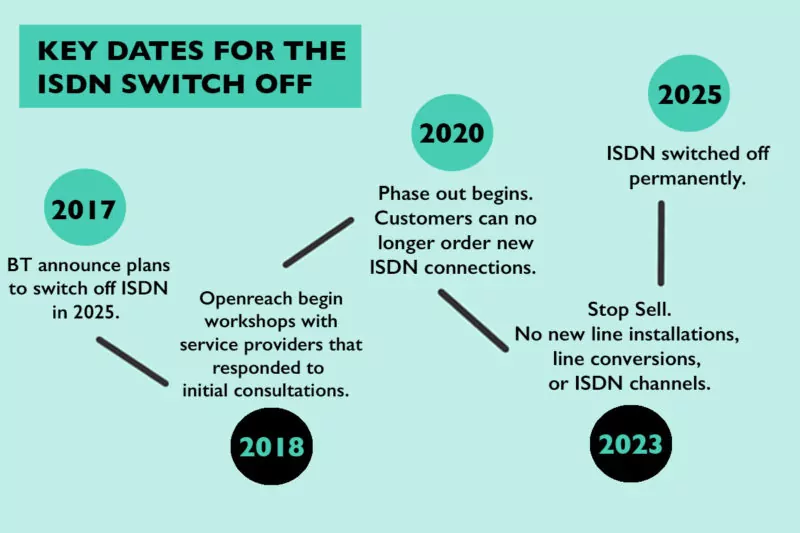
As the switch from ISDN to IP technology is so seamless, there isn’t that much of an impact nor is it something to worry about. The switch off is in two stages. From 2020, BT will no longer be taking new ISDN orders, but you can still use your preexisting one. You’ll have up to 5 years to make the switch and 2025 is when ISDN will be officially shut off – you should have made the switch by then!
If you’re an existing business who has an ISDN line, there’s plenty of time for you to make the switch. If you’re a new business just starting up, go straight for IP technology – which is your only choice as you can no longer purchase ISDN lines from 2020.
Whether you choose VoIP or SIP to make the switch, you will see a positive impact on your business communications and your business as a whole. Take a look at the main benefits for making the switch to IP technology:
Cost-effective
VoIP technology is significantly cheaper and requires less equipment than ISDN. It’s set up and running costs are much lower and they have more capacity to conduct a variety of calls. With VoIP, there is also less equipment and lines – one internet connection is all that’s needed to make and manage voice connections.
Disaster recovery
Disaster recovery is a set of policies and procedures that enables recovery and continuation of services and infrastructures. VoIP has great disaster recovery as all your data and functionality is provided in the cloud, ensuring there are little to no disruptions in service or loss of information. Essentially, if there were any issues with your phone system due to a power cut or a natural disaster, your VoIP service will offer a comprehensive disaster recovery service, including cloud backup, rerouting to business mobiles and remote access to your system. Our new hosted VoIP service, Wave, offers this.
Call features
VoIP have many additional call and media features which an ISDN line doesn’t offer. These features include auto attendants, voicemail to email, call queues, call recording, and more. VoIP also provides more ways to make a phone call, like mobiles, laptops, desktops and softphones, offering more mobility and flexibility.
Talk anywhere
As long as you have an internet connection, you can use VoIP anywhere. You can choose any number you like and make and manage calls wherever you are in the world. You don’t need to add any physical lines but just require an extension number. This is great for businesses who have remote workers or if you’re a startup and constantly on the go.
Will remote and hybrid workers be affected by the ISDN switch-off?
COVID-19 and lockdown measures massively impacted the way businesses work and communicate. In 2020, remote working was the norm and as we’ve been moving back to the office in 2021, hybrid working – a mix of remote and office work – has become the preferred choice.
According to a 2021 survey, the majority of UK SMEs haven’t been regarding the ISDN switch-off as a priority or considering the effect it could have on remote and hybrid workers. Remote workers could be severely affected and disrupted by the upcoming replacement of legacy communication services and lines. The list of devices that may be affected includes dial up devices, fax, building management systems and lines mainly used by phone systems.
Making the move to the cloud will significantly help remote and hybrid employees remain connected to their business and using digital tools and platforms put in place during lockdown. It’s vital to take action now in order to avoid disruption nearer the time – for both office and remote workers.
Glossary of key terms
Analogue
Analogue is a type of electrical signal that transmits information. With analogue technology, the information is translated into electric pulses of varying amplitude.
B-channel
A B-channel or a Bearer channel is a user channel on an ISDN circuit. It is used to carry voice and user data.
B-ISDN
B-ISDN stands for Broadband ISDN and is an ISDN standard that transmits voice and video data over fiber optic telephone lines.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is the maximum rate of data transferred during a given time period. It’s measure in bits per second.
BRI
BRI stands for Basic Rate Interface. It’s an ISDN configuration primarily used for voice-grade telephone services.
Cable
A cable is an assembly of wires that are used to carry an electrical current.
Channel
A channel is a communications path between two systems. It can transmit and receive information and data.
Circuit
A circuit is a physical path which electrical signals can pass through.
Codecs
A codec is a device or program that converts data packets of a segment of software or hardware, so it can be delivered, received, used, stored and encrypted. They do this by compressing or decompressing and encoding or decoding data packets.
D-channel
A D-channel or a Delta channel is a user channel on an ISDN circuit. It is a combination of data, packet networking and control and signaling.
Digital
Digital is a type of electrical signal that transmits information. With digital technology, the information is translated into a binary format where each bit is representative of two distinct amplitudes.
DOV
DOV stands for Data Over Voice and is a technology used for transmitting data and voice simultaneously over twisted-pair copper wiring or using an ISDN line.
DSL
A Digital Subscriber Line typically refers to an ISDN line. It’s a family of technologies that are used to transmit digital data over telephone lines.
DS0
Stands for Digital Service Zero. It’s a 64 kbp/s pipe used for data and signalling.
ISDN
Stands for Integrated Services Digital Network. It’s a set of communication standards that uses digital transmission to make phone calls, video calls, transmit data and other network services over the circuits of the traditional PSTN.
Interface
An interface specifies signaling and management functions between two networks.
K/bit
A kilobit per second is a unit of data transfer rate.
Line
A line is an electrical connection between a telephone service provider’s switch and a telephone terminal or key system. A line can be physical or virtual.
Modem
An abbreviation for modulator-demodulator. A modem is a hardware device that converts data into formats, suitable for transmission mediums, so it can be transmitted from computer to computer.
Packet
A packet is a collection of data that is used by computers to communicate with each other. The data is in the form of computer signals which are encapsulated and sent across the network.
PBX
Stands for Private Branch Exchange. It’s a private telephone network used within a company or organisation.
PRI
PRI stands for Primary Rate Interface and is used for carrying multiple Digital Signal 0 services and data between the ISDN network and a user.
Protocol
Protocol is a convention or procedure between two points during data communication.
PSTN
Stands for Public Switched Telephone Network.
Signaling
Signaling is the use of signals for controlling communications.
Transmission
Transmission is the process of sending and propagating an analogue or digital information signal over a physical point-to-point medium.
FAQs
What are ISDN lines?
ISDN is a set of communication standards that uses digital transmission to make calls, transmit data and other network services over the circuit of the PSTN. ISDN delivers a combination of voice, video and data over a single line. Multiple devices can be attached to this line.
What are the types of ISDN?
The two main types or ‘ISDN standard’ is BRI and PRI. Narrowband ISDN (N-ISDN) and Broadband ISDN (B-ISDN) are also ISDN standards but aren’t used as commonly.
What is the difference between ISDN and PSTN?
The main difference between ISDN and PSTN is that the former uses digital lines and the latter uses analogue lines. While they both transmit voice and data through a network on traditional copper lines, ISDN can run multiple channels and applications over a single line, unlike PSTN. Overall, ISDN is better quality and offers more services than PSTN.
What is the difference between ISDN and DSL?
Both an ISDN and a DSL (Digital Subscriber Line) work over the same kind of network, carrying signals over copper wires. The main difference between the two is that ISDN lines must be installed as they require an adapter at both ends of the line. A DSL uses existing telephone lines along with a modem. It doesn’t need installation of wires as long as there’s already a line in the home or organisation.
Why is ISDN being switched off?
ISDN is an outdated system which can no longer compete with VoIP and cloud-based systems. While ISDN still works, its infrastructure hasn’t changed since the 1980s and it doesn’t have the same kind of reach, features or quality of VoIP systems.
Is ISDN still available to purchase?
No. ISDN lines can still be used if you have one but as of 2020, you can no longer order a new ISDN line.
What are the key dates for the ISDN switch off?
The key dates for the ISDN switch off is 2020, 2023 and 2025. The ISDN ‘phase out’ begins in 2020, where you can no longer order new ISDN connections/lines. In 2023, there will be no new line installations, line conversions or channels. In 2025, ISDN will be switched off and you can no longer use it – you should have made the switch to VoIP or SIP by then.
What are the alternatives to ISDN?
ISDN will be replaced by IP technology, with VoIP and SIP being the best and preferred options.
What should businesses do to prepare for the switch off?
Right now, you don’t need to worry too much. But in the lead up to 2025, it’s a good idea to start looking at your options and figuring out what your business needs. From there, you can contact a provider and start to weigh up costs and features before switching all together.
SIP trunking or hosted VoIP?
Talk to our experts for a no-commitment consultation about your business communications.


